Rapid prototyping is all about quickly creating a scale model of a physical part.
It’s a way to make something using a 3D computer-aided design and fancy machines. We call it “rapid” because it’s hella fast compared to the old-school methods!
By using rapid prototyping, manufacturers can act quickly and find any problems that may arise. This helps reduce material waste and decreases the chances of costly mistakes during production.
So, how does rapid prototyping actually work?
Read on to find out more…
What Is Rapid Prototyping?
Rapid prototyping is a technique used to quickly create physical parts or assemblies using 3D CAD data.
It involves using 3D printing or additive layer manufacturing technology to build the part or assembly layer by layer. Unlike traditional methods, rapid prototyping doesn’t require tooling.
When people think of rapid prototyping, they often imagine 3D printing.
However, it also includes other processes like CNC machining, stamping, injection molding, and vacuum casting. These methods can be used at any stage of the product design process, from idea development to final testing.
The beauty of rapid prototyping is that it speeds up the development cycle and allows designers and engineers to test and refine their ideas quickly.
By iterating and refining designs rapidly, it becomes easier to identify and solve problems early on. This helps to reduce costs, minimize the risk of errors, and accelerate the time-to-market for new products.
In summary, rapid prototyping is a versatile and efficient method that enables designers and engineers to create physical prototypes quickly and effectively. It offers numerous benefits in terms of cost, time, and problem-solving. Overall, it’s a valuable tool for product development.
What Are The Benefits and Limitations of Rapid Prototyping?
Let’s delve into the benefits and limitations of rapid prototyping:
Benefits of Rapid Prototyping:
- Quick Visualization of Ideas: Rapid prototyping allows you to transform abstract ideas into tangible representations swiftly. This visual aspect helps both designers and stakeholders grasp the concept more easily.
- Early User Feedback: Creating a prototype early in the design process lets you gather feedback from users or clients before investing significant time and resources. This helps identify potential issues and make necessary adjustments early on.
- Reduced Development Time: Rapid prototyping accelerates the design and development process. It minimizes time spent on rework by catching design flaws early, resulting in faster iterations and quicker final product delivery.
- Effective Communication: Prototypes serve as a common language between designers, developers, and stakeholders. They make it easier to communicate design intentions and functionality expectations, reducing misunderstandings.
- User-Centered Design: By allowing users to interact with a prototype, you can better understand their needs and preferences, leading to a more user-centric final product.
- Iterative Improvement: Prototypes are designed to be iterated upon. This iterative approach enables constant refinement based on user feedback, evolving the design to meet user requirements effectively.
- Reduced Costs: Identifying design flaws early in the process helps avoid costly changes during later stages of development or after launch.
Limitations of Rapid Prototyping:
- Scope Limitation: Rapid prototypes often focus on specific aspects of the final product, potentially missing out on the big picture. They might not capture all features and interactions.
- Quality vs. Speed: The speed of rapid prototyping might sometimes compromise the depth and quality of certain design aspects or interactions.
- Misleading Realism: Depending on the fidelity of the prototype, users might mistake it for a final product, leading to skewed feedback or unrealistic expectations.
- Resource Intensive: Creating high-fidelity prototypes can demand significant time and resources. Additionally, changes made in the prototype might not seamlessly translate to the final product.
- Technical Challenges: Rapid prototyping might not fully consider the technical feasibility and limitations of implementation. Certain design elements might be difficult to replicate in the actual product.
- Feedback Overload: Gathering feedback from users and stakeholders can be both an advantage and a limitation. Too much feedback, or conflicting opinions, can lead to confusion and decision-making challenges.
- Potential Scope Creep: Frequent iterations can lead to the addition of new features or changes not originally planned, increasing the scope and potentially delaying the final product.
Essential Steps and Fundamentals of Rapid Prototyping
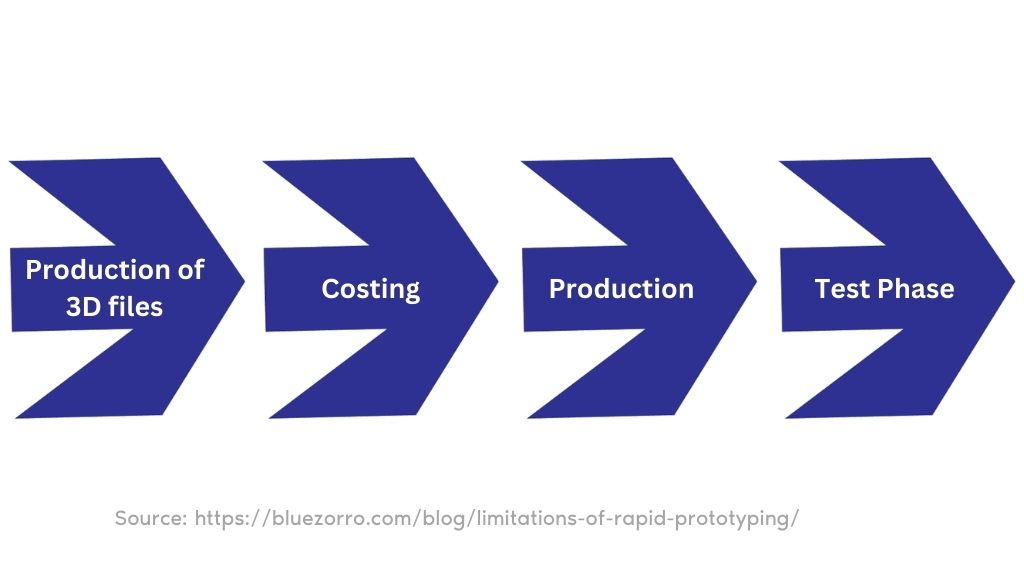
Step 1: Making the 3D Files
Alright, first things first – we’re diving into the world of rapid prototyping. The initial step is all about creating those 3D files for your product.
You’ve got a couple of options here: you can team up with specialized design offices to make those snazzy 3D files.
Oh, and don’t forget about crafting some 2D designs, especially if you’re dealing with parts that need super-precise measurements. Make sure you lay out all the specs too – these will depend on how the parts will be used and any tech limits.
Once those 3D files and specs are good to go, they’re off to rapid prototyping pros like LEADRP.
Step 2: Crunching the Numbers
Now, let’s talk money.
A top-notch prototyping crew takes a good look at your parts and their fancy technical features.
They’re figuring out how much this whole rapid prototyping deal will cost you. The fancy stuff they consider includes the materials, process, finishes, and the way everything’s put together.
And if the files need a little tweaking, that’s okay – changes can be made. To give you an accurate price tag for this rapid prototyping adventure, they’ll need a proper 3D part drawing.
Step 3: Time to Create
Once everyone’s nodded in agreement and given a thumbs-up to all the parts, it’s showtime!
Production kicks off, but sometimes it’s smart to make a few sample parts or plates before jumping into the whole rapid prototyping production shindig – especially if the files are a bit complex.
Step 4: Testing, Testing
All the parts are now out in the world, ready to shine. But hold on a sec – we’re not done just yet. It’s test time! We’ve got to make sure those parts meet all the requirements we set out from the get-go.
Here’s what we’re scrutinizing:
- How the prototypes look
- Their physical and mechanical traits
- Any visual features, even color specifics like Pantone and RAL references
- The dimensions, including sneaky things like diameters
- The snazzy finish
This step is like the superhero phase – it makes sure our final parts can actually do what we had in mind. If it turns out they’re not quite hitting the mark, no biggie. We just need to put in some extra work until they’re ready to rock.
Understanding The Importance of Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping is incredibly important because it allows companies to create and launch new products quickly to keep up with the fast-paced consumer market.
In today’s competitive business world, speed is essential to staying ahead.
That’s why rapid prototyping has become such a crucial part of the new product development process.
There are several reasons why rapid prototyping is so important.
First and foremost, it accelerates the entire product development process, saving time and resources.
By quickly creating prototypes, companies can test and iterate on their designs, speeding up the time it takes to bring a product to market.
Another key benefit of rapid prototyping is that it allows for early-stage design and concept validation. Companies can test the form, fit, and function of their designs early on, ensuring that they are on the right track before investing further resources.
Furthermore, rapid prototyping enables product validation in the final phase.
Companies can test their prototypes against technical requirements and business objectives to ensure that they meet the necessary criteria. This helps to minimize the risk of launching a product that doesn’t meet the desired goals.
In addition to these benefits, rapid prototyping also allows for functionality testing. This means that companies can validate the objectives of their concept and finalize the product specification. By testing the functionality of the prototype, companies can make any necessary adjustments before moving forward with production.
Understanding The Types of Rapid Prototyping Tests In a Hyper-Competitive Environment
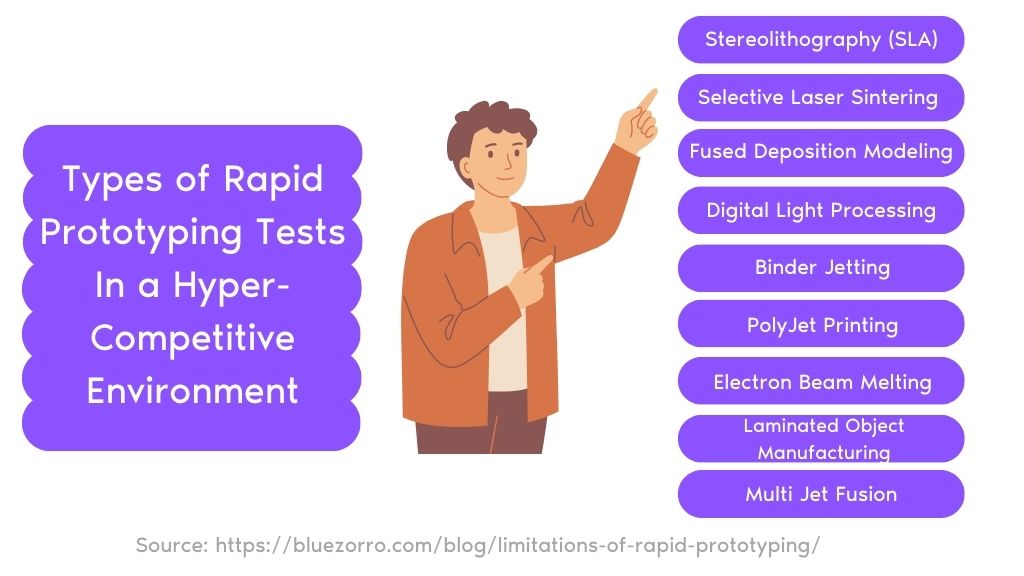
1. Stereolithography (SLA):
SLA is one of the oldest rapid prototyping techniques.
It uses a laser to solidify a liquid resin layer by layer, creating a 3D object. SLA is known for producing high-resolution, detailed prototypes and is widely used in industries like product design and medical devices.
2. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS):
SLS employs a laser to fuse powdered materials (like plastics, metals, or ceramics) layer by layer, forming a solid object.
It’s particularly useful for creating complex geometries and functional prototypes.
3. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM):
FDM is quite popular due to its accessibility. It extrudes thermoplastic material layer by layer to build the model.
It’s widely used for creating functional prototypes, concept models, and even end-use parts.
4. Digital Light Processing (DLP):
Similar to SLA, DLP uses a light source to solidify liquid photopolymer resin layer by layer.
DLP technology can be faster than traditional SLA, making it suitable for producing prototypes swiftly.
5. Binder Jetting:
This process involves depositing layers of powdered material (like sand) and then using a liquid binder to selectively bind the powder together, layer by layer.
It’s used for creating prototypes and even metal parts.
6. PolyJet Printing:
PolyJet combines inkjet printing and UV-curable resins.
It deposits layers of liquid photopolymers that are then cured by UV light. It’s known for its ability to produce highly detailed, multi-material prototypes.
7. Electron Beam Melting (EBM):
EBM uses an electron beam to melt metal powder, creating solid metal parts.
It’s particularly suitable for aerospace and medical applications where complex metal parts are required.
8. Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM):
LOM builds models by layering and bonding sheets of material, often paper or plastic. A laser or blade cuts each layer according to the design, and then they’re stacked to create the final prototype.
9. Continuous Liquid Interface Production (CLIP):
CLIP utilizes a liquid resin that’s solidified by a continuous light source and a tunable oxygen membrane.
It offers faster print speeds and high-quality parts compared to traditional SLA.
10. Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS):
DMLS is a metal 3D printing technique that uses a laser to fuse metal powder, layer by layer. It’s commonly used in aerospace, medical, and automotive industries for creating functional metal parts.
11. Multi Jet Fusion (MJF):
MJF uses a liquid binding agent and a detailing agent to fuse plastic powder layer by layer. It’s known for its speed and the ability to produce strong functional parts.
These are just a few examples of the rapid prototyping processes available today.
Each process comes with its own advantages and limitations, making them suitable for various applications and industries.
Conclusion:
Rapid prototyping is important because it allows you to create sample parts of your product.
These samples help you verify if components fit, function properly, are manufacturable, look good, and are strong enough. It’s a way to catch design defects early on in the product development process, so you can fix them.
But here’s the thing: the success of your rapid prototyping project largely depends on the machine shop you work with. You need a reliable and skilled partner.
That’s where we come in. We’re Blue Zorro, a leading company that specializes in providing managed IT services and consultation on various forefronts. We have a range of capabilities to meet your needs.
If you’re in need of rapid prototyping services consultation or anything else for that matter, don’t hesitate to reach out to us. We’re here to help. Contact us anytime, and we’ll be happy to discuss your project and provide the solutions you need.


